MicroPython
v1.27.0Features
-
Implements Python 3.4 syntax including exceptions, ‘with’, and ‘yield from’ statements.
-
Supports ‘async’ and ‘await’ keywords from Python 3.5 for asynchronous programming.
-
Includes a core Python compiler and runtime that can execute scripts directly on-device.
-
Provides a cross-compiler (mpy-cross) to turn scripts into precompiled bytecode (.mpy) for faster execution.
-
Supports freezing Python scripts into the firmware executable to significantly reduce memory usage.
-
Offers hardware-specific modules for low-level control of GPIO, Timers, ADC, DAC, and PWM.
-
Includes built-in support for communication protocols including SPI, I2C, UART, CAN, and I2S.
-
Provides networking capabilities through dedicated socket, ssl, and network modules.
-
Supports multithreading on select hardware ports via the _thread module.
-
Includes a comprehensive asyncio implementation for cooperative multitasking.
-
Features an interactive REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop) for real-time programming and debugging.
-
Supports on-device filesystems for script storage and data logging.
-
Provides specialized modules for Bluetooth (BLE) and USB Device functionality.
-
Allows extending the language with custom modules implemented in C via the extmod system.
-
Includes advanced hardware support for Pulse Counters and Quadrature Encoders on specific architectures.
-
Targets devices with as little as 256kiB flash and 16kiB RAM.
Architecture
MicroPython is designed with a highly modular architecture that separates the core Python language implementation from platform-specific hardware logic. The system is centered around the py/ directory, which contains the core compiler, runtime, and virtual machine (VM). This core is written in highly portable C and is responsible for parsing Python source code, generating bytecode, and managing the object model and garbage collection.
To support diverse hardware, MicroPython utilizes a Ports system. Each port (found in the ports/ directory) contains the glue code necessary to interface the core VM with a specific microcontroller’s Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) or an operating system. Additionally, the extmod/ directory provides optional C-based modules that implement non-core functionality, such as filesystem support, networking stacks, and specialized hardware protocols, ensuring that the core remains lean while allowing for feature-rich builds.
Core Components
- py/: The core Python implementation, including the compiler, runtime, and core library.
- mpy-cross/: A cross-compiler tool used to pre-compile Python scripts into bytecode for embedded execution.
- ports/: Platform-specific code for various architectures (e.g., STM32, ESP32, RP2).
- extmod/: Non-core modules implemented in C for performance and hardware access.
- lib/: Submodules for external dependencies and vendor-provided HALs.
Use Cases
This library is ideal for:
- IoT Development: Rapidly creating connected devices using high-level networking and security modules like
socket,ssl, andmqtt. - Rapid Prototyping: Using the interactive REPL to test hardware peripherals and logic in real-time without the need for a full compile-flash-reboot cycle.
- Education: Teaching Python programming and electronics simultaneously on affordable, physical hardware.
- Industrial Automation: Implementing complex control logic, sensor data processing, and communication protocols (CAN, Modbus) on robust microcontroller platforms.
- Embedded Scripting: Adding a user-accessible scripting interface to existing C/C++ projects by embedding the MicroPython engine.
- Low-Power Monitoring: Utilizing deep-sleep modes and hardware interrupts to create battery-operated sensor nodes.
Getting Started
To begin developing with MicroPython, the first step is typically to build the cross-compiler by running make within the mpy-cross/ directory. Following this, you can navigate to the specific port directory corresponding to your hardware (e.g., ports/stm32/) and run make submodules followed by make to generate the firmware image. Once flashed, the device provides a Read-Eval-Print Loop (REPL) over a serial connection, allowing for immediate Python command execution.
Comprehensive documentation, including API references for hardware-specific modules like machine and network, is available at the official MicroPython documentation site. For community support and project discussions, developers are encouraged to use the GitHub Discussions and the official Discord server.
Related Projects (11)
Awesome CircuitPython
A curated collection of resources for CircuitPython, an Adafruit-supported fork of MicroPython designed for education and prototyping on microcontrollers. It provides a comprehensive directory of libraries, hardware support, tutorials, and community tools for the Python-on-hardware ecosystem.
Awesome Zephyr RTOS
A curated collection of high-quality resources, libraries, tools, and learning materials for the Zephyr RTOS ecosystem. It serves as a comprehensive directory for developers looking for official documentation, community-supported libraries, and hardware platforms compatible with Zephyr.
Blinker IoT Documentation
The official documentation repository for the Blinker IoT platform, providing comprehensive guides for connecting embedded devices to the cloud. It supports a wide range of hardware including ESP32, ESP8266, and Arduino, with SDKs for FreeRTOS, Python, and Node.js.
Broccoli
Broccoli is a distributed task queue framework designed for ESP32 clusters, enabling parallel task execution across multiple MicroPython-based nodes. Inspired by Celery, it provides a scalable way to manage workloads in embedded environments using a cluster of low-cost microcontrollers.
esp32-cam-micropython
A specialized MicroPython port for the ESP32-CAM module that integrates camera support directly into the firmware. It features a custom C-based camera module, support for LittleFS to optimize RAM usage, and includes various asynchronous web server examples for streaming video and capturing images.
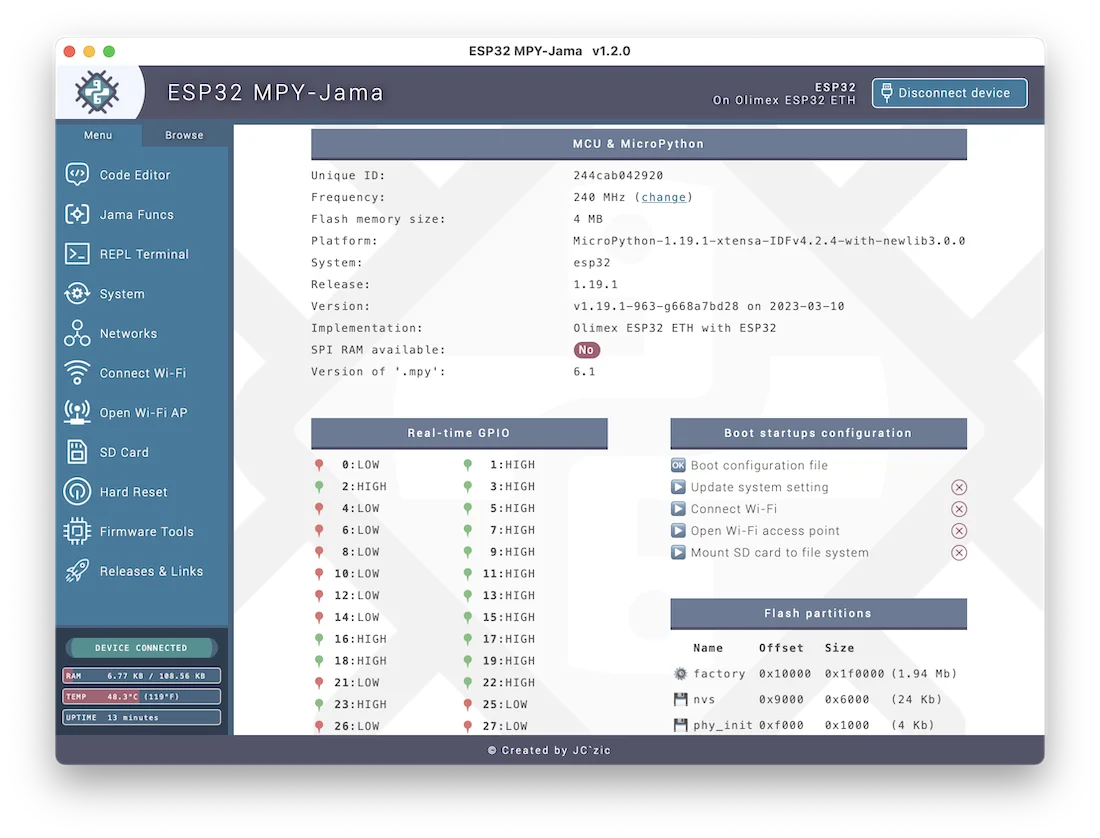
ESP32 MPY-Jama
ESP32 MPY-Jama is a cross-platform desktop IDE and management tool designed for Espressif ESP32 microcontrollers running MicroPython. It provides a graphical interface for file management, real-time system monitoring, network configuration, and firmware flashing. The project simplifies IoT development by offering built-in 'Jama Funcs' for rapid testing of peripherals like sensors, LEDs, and displays.
LVGL Blog
The official blog repository for the LVGL (Light and Versatile Graphics Library) project, featuring technical articles, release notes, and hardware reviews. It serves as a community hub for sharing experiences, porting guides, and GUI development tips using LVGL on various embedded platforms.
MCUDev Black STM32F407VET6 MicroPython Support
This repository provides the board definition files required to run MicroPython on the MCUDev Black STM32F407VET6 development board. It includes hardware-specific configurations for the STM32F407VET6 MCU, onboard SPI Flash, SD card slot, and various peripheral headers.
MicroPython Encoder Menu
A lightweight, asynchronous menu system for MicroPython designed for rotary encoders and OLED displays. It provides a flexible framework for creating submenus, handling user input, and managing non-blocking tasks on platforms like the Raspberry Pi Pico and ESP32.
PyEspCar - MicroPython-ESP32 WIFI Car
PyEspCar is an open-source robotics platform based on the ESP32 and MicroPython, designed for computer vision and motion control education. It features a dual-layer metal chassis, a 2-DOF gimbal for camera mounting, and supports remote debugging via WebREPL and MQTT control.