MicroPython TM1637 Library
A MicroPython library for quad 7-segment LED display modules using the TM1637 LED driver. It provides a comprehensive API for controlling brightness, displaying numbers, hex values, temperatures, and scrolling text on various microcontroller platforms.
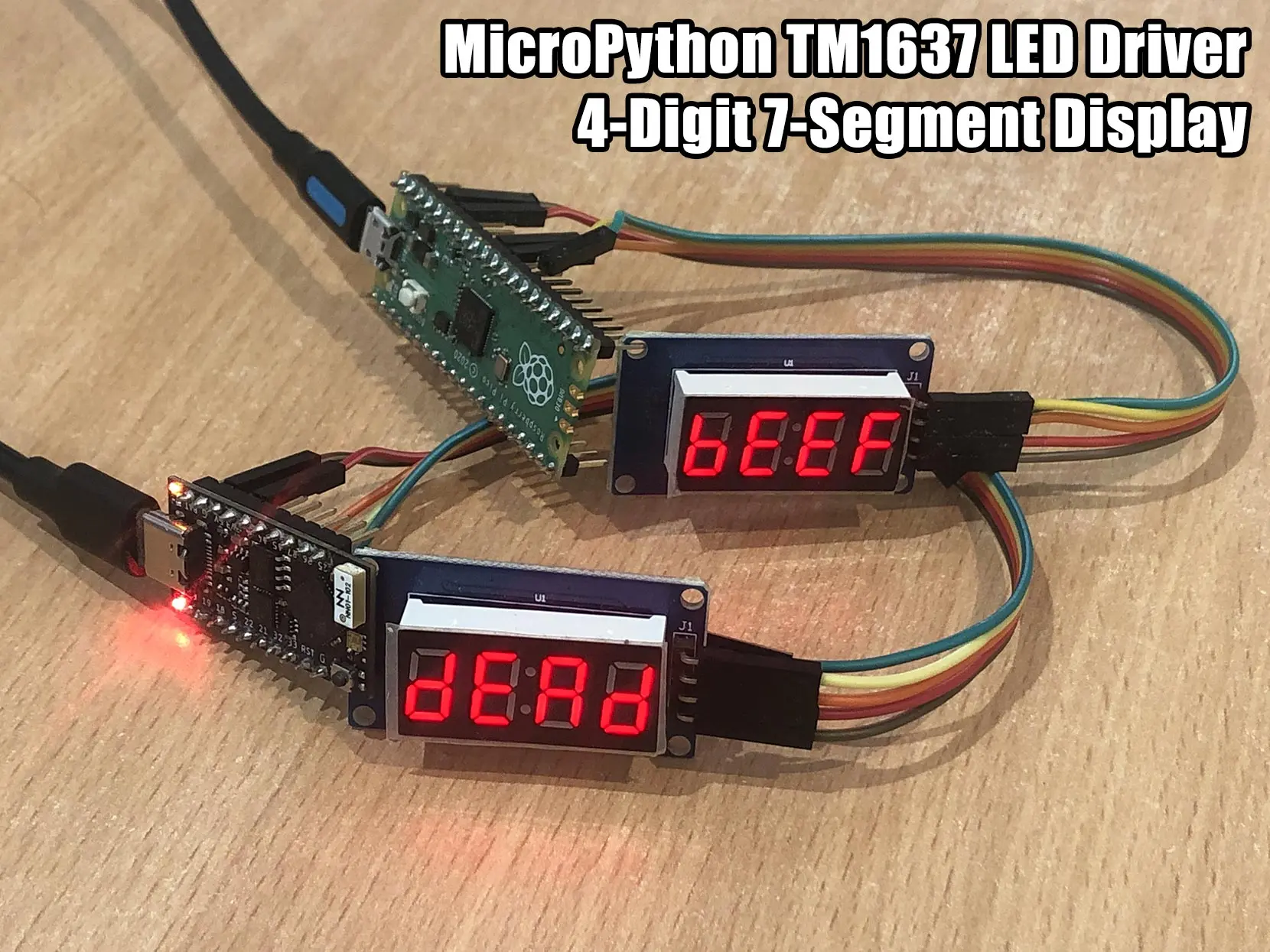
Overview
The MicroPython TM1637 library provides a robust interface for controlling quad 7-segment LED display modules. These modules, commonly used in clocks, timers, and simple numeric readouts, rely on the TM1637 driver chip. This library abstracts the low-level bit-banging required to communicate with the driver, offering a high-level Pythonic API for developers working with MicroPython-compatible hardware.
Key Features
The library is designed to be versatile, supporting a wide range of display tasks beyond simple digit output. Key capabilities include:
- Brightness Control: Adjust the display intensity across 8 levels (0-7).
- Flexible Data Entry: Display integers, hexadecimal values, and formatted strings.
- Specialized Formatters: Built-in methods for displaying temperatures (with degree symbols) and time (using the colon segment).
- Text Effects: Support for scrolling strings across the display, which is particularly useful for 4-digit modules showing longer messages.
- Custom Segment Control: Direct access to individual segments for creating custom characters or symbols.
Hardware Compatibility
Because the library uses bit-banged GPIO for the Clock (CLK) and Data I/O (DIO) lines, it is compatible with virtually any MicroPython-supported board. The documentation provides tested connection examples for several popular platforms:
- Raspberry Pi Pico: Using IO27 (CLK) and IO26 (DIO).
- TinyPICO (ESP32): Using IO18 (CLK) and IO23 (DIO).
- WeMos D1 Mini (ESP8266): Using D1 (CLK) and D2 (DIO).
The library has been verified with various hardware modules, including the Seeed Studio Grove 4-Digit Display, RobotDyn 4-digit and 6-digit tubes, and generic TM1637 modules found on common electronics marketplaces.
Technical Implementation
The driver handles the specific timing requirements of the TM1637 protocol, including start/stop signals and byte-level transmission with acknowledgment cycles. It includes a comprehensive segment map for the standard 7-segment font, covering numbers 0-9 and a basic alphabet (A-Z, though limited by the physical segments available).
For modules that feature a decimal point after every digit instead of a central colon, the library provides a specialized TM1637Decimal class. This subclass overrides the string encoding logic to correctly handle the 8th bit (MSB) of each segment, which typically controls the decimal point on those specific hardware variants.
Getting Started
Basic initialization requires defining the pins used for the clock and data lines. Once initialized, displaying data is straightforward:
import tm1637
from machine import Pin
# Initialize the display
tm = tm1637.TM1637(clk=Pin(5), dio=Pin(4))
# Show a simple string
tm.show('help')
# Display a number
tm.number(-123)
# Display temperature
tm.temperature(24)
# Show hex values
tm.hex(0xbeef)For more advanced use cases, such as creating custom animations or handling specific segment layouts, the write() method allows passing raw byte arrays directly to the driver.