MicroPython for Monocle
A custom MicroPython firmware deployment specifically designed for the Monocle AR glasses. It integrates the Nordic nRF52832 SoC with support for Bluetooth LE, FPGA-driven displays, and camera modules using the LittleFS file system and Nordic SoftDevice.
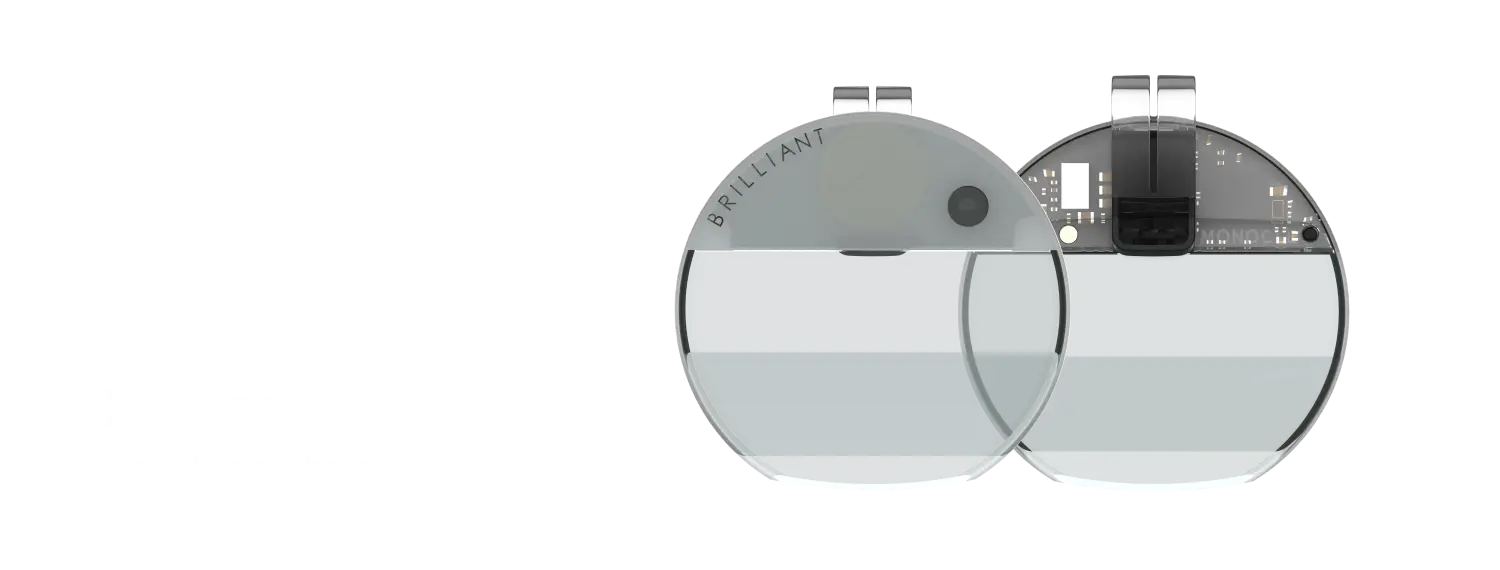
Overview
MicroPython for Monocle is a specialized firmware deployment designed for the Monocle AR glasses developed by Brilliant Labs. This project provides a high-level Python-based environment for interacting with the Monocle’s sophisticated hardware, including its display, camera, and Bluetooth capabilities. By porting MicroPython to this platform, developers can rapidly prototype AR applications using Python scripts rather than low-level C code.
Hardware Integration
The firmware is built to run on the Nordic Semiconductor nRF52832 SoC, which handles the core logic and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) connectivity. The architecture is designed to interface with several key components:
- FPGA Interface: Monocle uses an FPGA to drive its display and handle high-speed data from the camera. The MicroPython port includes specific modules to communicate with and reset the FPGA.
- Camera Support: Integration for the OV5640 camera module allows for image capture and processing through Python APIs.
- Display and Graphics: The project includes
libvgrs, a vector graphics library, and custom modules for rendering 2D graphics on the Monocle’s display. - Sensors and I/O: Support for touch sensors, microphones, and LED control is built directly into the MicroPython environment.
Technical Implementation
The project leverages the Nordic SoftDevice S132 for BLE functionality, enabling a wireless REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop). This allows developers to send Python commands to the glasses over Bluetooth in real-time. For persistent storage, the firmware utilizes the LittleFS (LFS2) filesystem, ensuring robust data management on the device’s internal flash memory.
The build system is based on a standard Makefile and requires the ARM GCC Toolchain and nRF Command Line Tools. It integrates the nrfx driver layer to manage peripherals like I2C (TWIM), SPI (SPIM), and SAADC for battery monitoring.
Key Features
- Wireless Development: Full REPL access over BLE, allowing for interactive coding without physical cables.
- Custom Python Modules: Includes specialized modules such as
bluetooth,camera,display,fpga,led, andtouchto expose hardware features to the Python environment. - Vector Graphics: Integrated 2D vector graphics support via the
modvgr2dmodule. - Debugging Tools: Built-in support for Segger RTT (Real Time Transfer) for high-speed logging and debugging during development.
Getting Started
Developers looking to modify the firmware can build the project using the provided Makefile. The process involves initializing submodules (including the core MicroPython repository), building the mpy-cross compiler, and then compiling the main application. The final firmware is typically packaged as a .hex file for initial flashing or a .zip DFU (Device Firmware Update) package for wireless updates using nrfutil.